AC-VC Topical Seminar #1
 Covid-19 Impact – What Can Be Learned from Satellite Observations & Emission Changes
Covid-19 Impact – What Can Be Learned from Satellite Observations & Emission Changes
The CEOS Atmospheric Composition Virtual Constellation (AC-VC) is pleased to invite you to our first virtual Topical Seminar on 13 July 2021 at 13:-00-15:30 UTC (06:00-08:30 US PDT, 09:00-11:30 US EDT, 15:00-17:30 CEST, 22:00-00:30 KST/JST).
The seminar will begin with an invited talk (30 min presentation + 10 min Q&A) followed by a series of short talks (7 min presentation + 3 min Q&A). A block of 30 min is reserved for general discussion.
How to Participate: Connection Details, Meeting Protocols, & Technical Guidance
Draft Agenda
|
ID |
Title |
Presenter |
Time |
|
1 |
The global impacts of COVID-19 lockdowns on urban air pollution: A critical review and recommendations [ Presentation ] |
Georgios Gkatzelis (FZJ) |
30 |
|
|
Q&A on invited talk |
|
10 |
|
2 |
Observed free tropospheric ozone changes and their attribution through model simulations [ Presentation ] |
Wolfgang Steinbrecht (DLR) |
10 |
|
3 |
Global tropospheric ozone responses to reduced NOx emissions; Air quality response in China; Feedbacks between atmospheric chemistry and climate change [ Presentation ] |
Miyazaki Kazuyuki (JPL) |
10 |
|
4 |
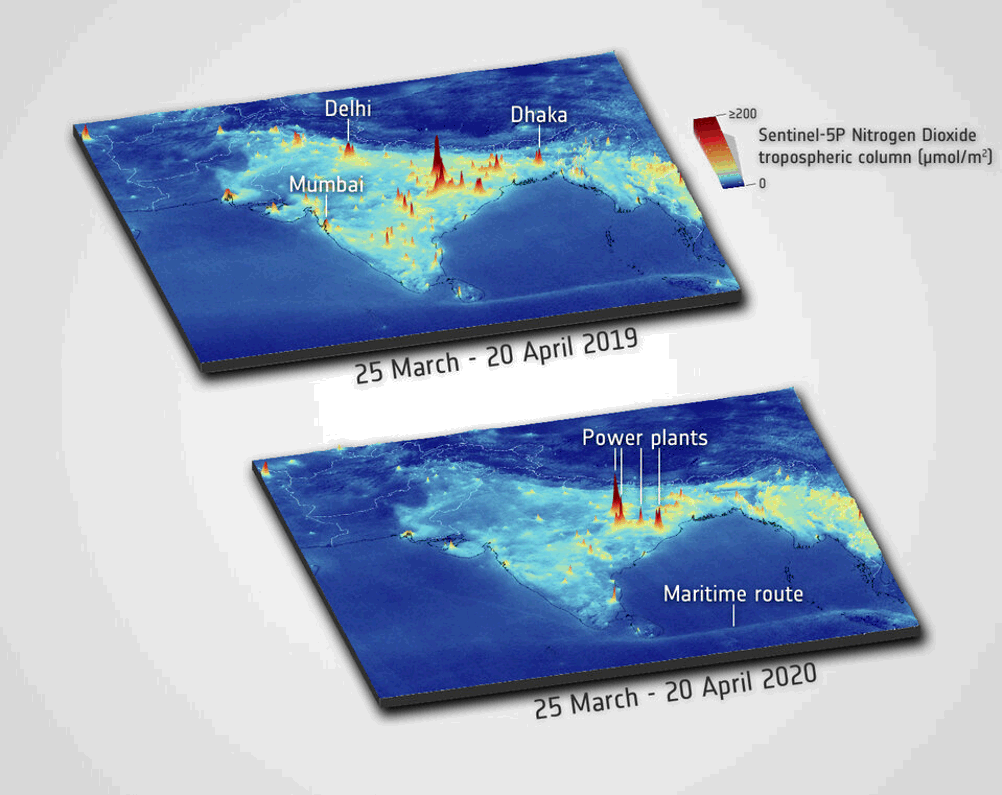
Reductions of NO2 Air Pollution during Covid-19 Lockdowns as Observed by Sentinel-5P TROPOMI [ Presentation ] |
Henk Eskes (KNMI) |
10 |
|
5 |
COVID-19 induced new normal urban air quality in the United States: correlating NOx emissions derived from fuels with TROPOMI NO2 [ Presentation ] |
Shobha Kondragunta (NOAA) |
10 |
|
6 |
Estimating lockdown-induced European NO2 changes using satellite and surface observations and air quality models [ Presentation ] |
Jerome Barré (ECMAWF) |
10 |
|
7 |
Regional Impacts of COVID-19 on Carbon Dioxide Detected Worldwide from Space [ Presentation ] |
Lesley Ott (NASA) |
10 |
|
8 |
Effects of COVID-19 lockdowns on fine particulate matter concentrations [ Presentation ] |
Melanie Hammer (WUSTL) |
10 |
|
|
General discussion |
|
30 |
References
Hammer, M.S., A. van Donkelaar, R.V. Martin, E.E. McDuffie, A. Lyapustin, A.M. Sayer, C.N. Hsu, R.C. Levy, M.J. Garay, O.V. Kalashnikova, and R.A. Kahn, 2021. Effects of COVID-19 lockdowns on fine particulate matter concentrations. Science Advances (in press)
Georgios I. Gkatzelis; Jessica B. Gilman; Steven S. Brown; Henk Eskes; A. Rita Gomes; Anne C. Lange; Brian C. McDonald; Jeff Peischl; Andreas Petzold; Chelsea R. Thompson; Astrid Kiendler-Scharr, The global impacts of COVID-19 lockdowns on urban air pollution: A critical review and recommendations, Elementa: Science of the Anthropocene (2021) 9 (1): 00176. https://doi.org/10.1525/elementa.2021.00176
Shobha Kondragunta, Zigang Wei, Brian McDonald, Dan Goldberg, and Daniel Tong. COVID-19 induced new normal urban air quality in the United States, JGR-Atmospheres in review
Miyazaki, K., K. Bowman, T. Sekiya, M. Takigawa, J. Neu, K. Sudo, G. Osterman, H. Eskes, Global tropospheric ozone responses to reduced NOx emissions linked to the COVID-19 world-wide lockdowns, Science Advances, Vol. 7, no. 24, eabf7460, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abf7460, 2021
Miyazaki, K., Bowman, K., Sekiya, T., Jiang, Z., Chen, X., Eskes, H., Ru, M., Zhang, Y., Shindell, D., (2020). Air quality response in China linked to the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID‐19) lockdown. Geophysical Research Letters, 47, e2020GL089252. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL089252
Laughner et al., Societal shifts due to COVID-19 reveal large-scale complexities and feedbacks between atmospheric chemistry and climate change, in review
Brad Weir, David Crisp, Christopher O’Dell, Sourish Basu, Abhishek Chatterjee, Tomohiro Oda, Lesley Ott, Steven Pawson, Benjamin Poulter, Zhen Zhang, Philippe Ciais, Steven Davis, Zhu Liu, Regional Impacts of COVID-19 on Carbon Dioxide Detected Worldwide from Space, Physics > Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.12740